Introduction to Mount Rinjani
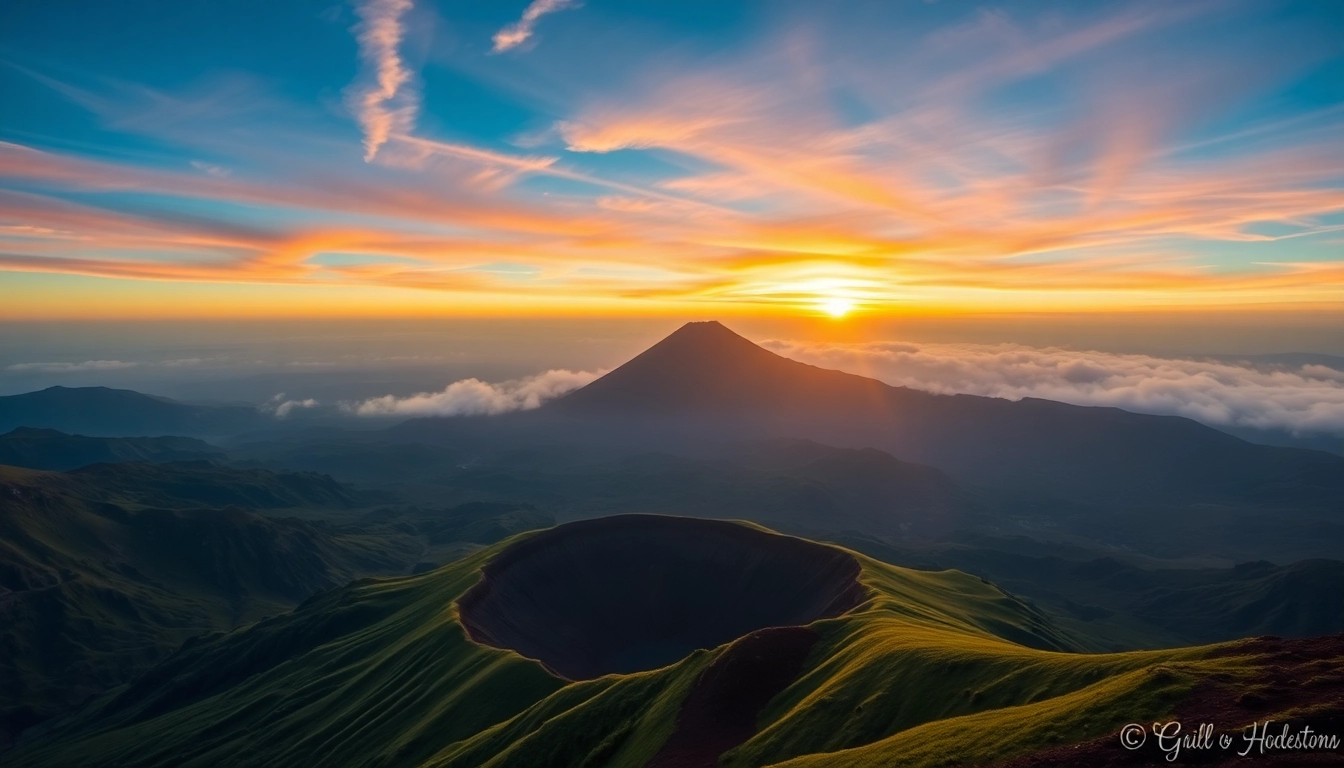
Perched majestically on the island of Lombok, Indonesia, Mt. Rinjani stands as one of the most iconic and challenging volcanic peaks in Southeast Asia. With an elevation of 3,726 meters, it is the second highest volcano in Indonesia, boasting a landscape rich in ecological diversity, cultural significance, and adventure opportunities. For centuries, Rinjani has been a focal point of local indigenous culture and a magnet for explorers worldwide seeking both natural beauty and spiritual connection. Whether you’re a seasoned trekker or an avid traveler eager to explore Indonesia’s volcanic heart, understanding the grandeur and complexity of Mount Rinjani is essential for appreciating its significant role in Indonesia’s geographical and cultural tapestry.
Location and Significance in Indonesia
Situated in West Nusa Tenggara, Lombok’s Mount Rinjani is nestled within the Gunung Rinjani National Park, which spans over 41,330 hectares. The mountain’s strategic position in this biologically diverse park makes it a key ecological zone, home to unique flora and fauna that have adapted to the volcanic environment. Its location not only marks it as a prominent natural landmark but also as a vital water source, with several crater lakes and hot springs contributing to local agriculture and daily life.
Despite being overshadowed by Indonesia’s more famous volcanoes like Mount Merapi or Mount Bromo, Rinjani’s prominence is underscored by its dual role as a natural wonder and a cultural symbol. Its presence influences local traditions, spiritual practices, and community livelihoods, emphasizing its importance beyond just geological features. Moreover, Rinjani’s status as an active volcano underscores the need for ongoing monitoring and study to understand its behavior and potential impacts on the surrounding communities and ecosystems.
Historical and Cultural Importance
Rinjani holds deep spiritual significance for Lombok’s indigenous Sasak and Balinese communities. Historically, it has been revered as a sacred site, considered a dwelling place of ancestors and gods. Traditional rituals and festivals are often held in its vicinity, especially around the crater lake, Segara Anak, which is believed to be inhabited by spirits. The mountain’s mythological lore has been passed down through generations, reinforcing its sacred status and fostering respectful coexistence with its volatile nature.
Throughout history, Mount Rinjani has also played a role in trade and migration routes across Southeast Asia. Its volcanic activity, while sometimes destructive, has enriched the soil, fostering thriving agricultural practices that sustain local populations. The site also features archaeological artifacts and cultural relics, revealing the mountain’s longstanding prominence in regional history. The melding of natural grandeur and spiritual reverence continues to shape the identity of Lombok and its inhabitants today.
Key Features and Highlights
- Crater Lake (Segara Anak): A stunning turquoise lake nestled within the volcano’s caldera, measuring approximately 170 meters deep. It is a focal point of natural beauty and cultural significance, with hot springs believed to have healing properties.
- Gunung Rinjani Summit: The primary target for trekkers, offering panoramic views of Lombok, the nearby islands, and even Bali on clear days. Reaching the summit requires stamina and acclimatization but offers a rewarding experience.
- Hot Springs and Waterfalls: Rich geothermal activity gives rise to various hot springs around the mountain, perfect for relaxation after a trek. Waterfalls, such as Sendang Gila and Benang Stokel, embellish the surrounding forests, offering scenic excursions.
- Ecological Diversity: The mountain ecosystem varies from lush rainforests at lower elevations to alpine-like environments closer to the summit, hosting endemic species and a rich variety of plants and animals.
Climbing Mount Rinjani: Trekking Essentials
Preparation and Necessary Skills
Embarking on a trek to Mount Rinjani demands meticulous preparation. Its challenging terrain and unpredictable weather require physical fitness, acclimatization, and proper gear. Trekkers should ideally possess experience in high-altitude mountains, though guided tours often accommodate beginners with sufficient training.
Physical preparation involves cardiovascular conditioning, leg strengthening, and stamina-building exercises. Familiarity with trekking equipment such as trekking poles, sturdy hiking boots, layered clothing, thermal wear, and rain protection is essential. Since weather can change rapidly, bringing windproof and waterproof gear ensures safety and comfort.
Altitude acclimatization is crucial to avoid altitude sickness, especially since the summit is nearly 3,726 meters above sea level. Spending extra days at intermediate campsites like Plawangan or Senaru can significantly reduce health risks.
Guided Treks and Tour Options
Although independent treks are possible, most travelers opt for guided tours due to the mountain’s demanding nature and the need for local expertise. Several reputable tour operators offer packages that include transportation, permits, guides, porters, and accommodations.
Guided treks typically range from 3 to 4 days, depending on the route and pace. Popular routes include the Sembalun and Senaru trails, both offering distinct scenery and challenges. Guided tours also provide logistical support, interpretative commentary, and safety management, making the experience accessible and enriching for all levels of hikers.
For planning purposes, the cost of guides can vary but generally falls within the range of Rp. 350,000 to Rp. 500,000 per day, with additional charges for porters and permits. It is advisable to book through reputable agencies that emphasize safety, ecological responsibility, and community engagement.
Challenges and Safety Tips
Climbing Rinjani presents several challenges, including altitude sickness, unpredictable weather, steep terrains, and physical exhaustion. Proper planning, awareness, and respect for nature are fundamental to a safe trek.
- Weather Awareness: Prepare for sudden rain, wind, or cold temperatures, especially near the summit. Always check weather forecasts before departure.
- Health Precautions: Stay hydrated, practice good hygiene, and ascend slowly to acclimate properly.
- Navigation Skills: Follow established trails and heed guide instructions. Use maps and GPS devices if trekking independently.
- Environmental Responsibility: Minimize ecological impact by sticking to designated paths and avoiding littering.
In case of emergencies, the proximity of rescue services within the park, coupled with guided experience, significantly improves response times. Carrying a basic first aid kit, communication devices, and informing someone of your itinerary further enhances safety.
Understanding the Rinjani Ecosystem and National Park
Flora and Fauna of Rinjani
The biodiversity within the Gunung Rinjani National Park is remarkable. At lower elevations, dense tropical rainforests host species like the Rinjani honeybee, Java sparrow, and various endemic orchids. As altitude increases, plant life transitions into montane forests with mosses, lichens, and hardy herbaceous plants adapted to cooler conditions.
Near the crater lake, unique ecosystems support species such as the Rinjani scops owl, Lombok forest lizard, and the endemic Rinjani Magpie. Birdwatchers and biologists value this habitat for its endemic and endangered species, which require careful habitat preservation efforts.
Conservation Efforts and Regulations
To preserve its ecological integrity, the Indonesian government established the Gunung Rinjani National Park, enforcing regulations that limit logging, hunting, and littering. Visitors are required to obtain permits, pay entrance fees, and adhere to park rules designed to minimize environmental impact.
Conservation projects focus on reforestation, monitoring of endemic species, and community engagement programs. Visitors play a pivotal role in supporting eco-tourism initiatives that benefit local communities and promote sustainable tourism practices.
Must-Visit Spots Inside the Park
- Segara Anak Lake: The central crater lake, renowned for its breathtaking beauty and thermal springs.
- Sendang Gila Waterfall: A scenic waterfall accessible via a short trek, perfect for cooling off and appreciating lush surroundings.
- Hill of Sunset (Puncak Monyet): Offers spectacular sunset views over the caldera.
- Rinjani Summit: The ultimate goal for many trekkers seeking panoramic vistas.
Best Time to Visit and Visitor Information
Optimal Seasons for Trekking
The ideal time to explore Mount Rinjani is during the dry season, typically from May to September. During these months, the weather is relatively stable, with clear skies and minimal rainfall, providing safe and rewarding trekking conditions.
Avoid the rainy season (October to April), when frequent rainstorms, fog, and mudslides increase risks and complicate navigation. However, some experienced trekkers do venture out during the shoulder months, equipped with proper gear and contingency plans.
Permits and Entry Requirements
All visitors intending to trek Mount Rinjani must secure permits from the park authorities. This includes paying an entrance fee, which contributes to park maintenance and conservation efforts.
Guided trekkers typically arrange permits through their tour operators, who handle all bureaucratic requirements. Independent trekkers should visit the park’s official offices or authorized agencies to obtain necessary documentation beforehand.
Entry is restricted for safety during volcanic activity or adverse weather, emphasizing the importance of monitoring volcano updates via official channels.
Travel Tips and Local Amenities
To enhance your Rinjani adventure, consider the following tips:
- Book guided tours well in advance, especially during peak season.
- Pack layered clothing, sturdy boots, and essential trekking gear.
- Carry sufficient water, snacks, and a portable stove if camping.
- Respect local customs and the mountain’s sacred sites.
- Stay updated on volcanic activity alerts from official sources.
- Utilize local accommodations in Senaru or Sembalun for pre-and post-trek stays.
Nearby amenities include cafes, shops, and small hotels in Sembalun and Senaru villages, which serve as starting points for treks and provide essential supplies.
Recent Volcanic Activity and Future Outlook
Historical Eruptions and Their Impact
Mount Rinjani’s history of eruptions reflects its active status, with notable activity recorded as recent as December 2015, which included ash plumes rising to 6 km altitude and lava flows. These eruptions have temporarily disrupted access, caused ash fall in surrounding areas, and necessitated evacuations.
The volcano’s activity is closely monitored by Indonesia’s Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, employing seismographs, thermal imaging, and satellite data to anticipate future eruptions. While eruptions pose risks, they also contribute to the renewal of the mountain’s landscape, creating new crater lakes and enriching soil fertility.
Monitoring and Risk Management
Rinjani’s status as an active volcano warrants continuous surveillance. The park authorities, in collaboration with geological agencies, issue volcano activity updates and evacuation advisories. Visitors should stay informed through official channels and heed all safety warnings.
Emergency preparedness, including knowing evacuation routes and having communication devices, is vital for trekkers. In periods of heightened activity, all tours are often suspended until conditions stabilize.
What Visitors Need to Know for Safe Engagement
While the thrill of observing an active volcano from close quarters is alluring, safety comes first. Always trek with licensed guides, follow park rules, and respect the mountain’s sacred status. Be prepared for changing weather, altitude challenges, and volcanic alerts.
Engaging with local communities sensitively and supporting sustainable tourism practices ensures that Mount Rinjani remains a natural and cultural treasure for generations to come. Remember, the mountain’s power and beauty require our utmost respect and vigilance.